Circuit breakers play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. By protecting circuits from electrical overloads, short circuits, and ground faults, circuit breakers help prevent damage to equipment and reduce the risk of electrical fires. In this article, we will delve into the basics of circuit breakers, explore different types available, understand their functions, and discuss how to select the right circuit breaker for your needs. Additionally, we will provide maintenance and troubleshooting tips to ensure your circuit breakers are always in good working condition.
The Basics of Circuit Breakers
When it comes to electrical systems, safety is of utmost importance. One crucial component that ensures the protection of these systems is the circuit breaker. Let’s dive deeper into what a circuit breaker is and why it plays such a vital role in maintaining electrical safety.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is an electrical device that acts as a safety switch. Its primary function is to automatically interrupt the flow of current in a circuit when it detects an electrical overload, short circuit, or ground fault. By doing so, it prevents excessive current from flowing through the circuit, which can cause damage to equipment and pose a significant risk of electrical hazards.
Imagine a scenario where an electrical circuit is experiencing an overload due to a sudden surge in current. Without a circuit breaker, the excessive current could lead to overheating, damaging the equipment and wires connected to the circuit. In severe cases, this overheating could even result in electrical fires, putting lives and property at risk.
However, with the presence of a circuit breaker, the situation is entirely different. As soon as the circuit breaker detects an overload or any other fault, it swiftly interrupts the flow of current, breaking the circuit. This action effectively prevents any further damage from occurring and ensures the safety of the electrical system.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Essential Electrical Supplies for DIY Projects
Why are Circuit Breakers Important?
Now that we understand what a circuit breaker does, let’s explore why it is so crucial for the safety and protection of electrical systems.
First and foremost, circuit breakers act as a defense mechanism against electrical overloads and short circuits. As mentioned earlier, these events can lead to overheating and potential fires. By interrupting the flow of current, circuit breakers prevent these hazardous situations from escalating, keeping both people and property safe.
Additionally, circuit breakers help in maintaining the smooth functioning of electrical systems. Imagine a scenario where a fault occurs in a circuit, causing a short circuit. Without a circuit breaker, the entire circuit would be compromised, resulting in a complete loss of power. However, with a circuit breaker in place, only the faulty section of the circuit is disconnected, allowing the rest of the system to continue operating uninterrupted.
Furthermore, circuit breakers provide convenience and ease of use. In the event of a fault, all it takes is resetting the circuit breaker to restore power. This eliminates the need for complex and time-consuming troubleshooting processes, making it more efficient for both professionals and homeowners.
In conclusion, circuit breakers are an integral part of electrical systems, ensuring safety, protection, and uninterrupted functionality. By promptly detecting and interrupting faults, they prevent potential hazards and keep electrical systems running smoothly. So, the next time you flip a switch or plug in an appliance, remember the vital role that circuit breakers play in keeping you safe.
Different Types of Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is an essential component in electrical systems that helps protect against overloads and short circuits. There are several different types of circuit breakers available, each with its own unique operating principle and features. In this article, we will explore three common types of circuit breakers: thermal circuit breakers, magnetic circuit breakers, and hybrid circuit breakers.
Thermal Circuit Breakers
Thermal circuit breakers, also known as bimetallic circuit breakers, rely on the principle of heat expansion to trip and interrupt the circuit. Inside the breaker, two different metals with different expansion rates are in contact with each other. When an excessive current passes through, the metals heat up, causing them to expand and separate, thus breaking the circuit.
These types of circuit breakers are commonly used in residential and commercial applications. They are reliable and cost-effective solutions for protecting circuits from overloads. The bimetallic strip used in thermal circuit breakers is carefully designed to ensure accurate and consistent tripping at specific current levels.
Magnetic Circuit Breakers
Magnetic circuit breakers, also called magnetic-hydraulic circuit breakers, work on the principle of electromagnetism. They contain a solenoid coil that generates a magnetic field. When a large current flows through the circuit, the magnetic field created by the solenoid coil attracts a plunger, causing the contacts to open and the circuit to break.
These circuit breakers are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where higher current levels are present. They offer fast and reliable protection against short circuits and can handle high inrush currents without tripping. The magnetic trip mechanism provides instantaneous response, ensuring that the circuit is quickly interrupted to prevent any damage or hazards.
Hybrid Circuit Breakers
Hybrid circuit breakers combine the features of both thermal and magnetic circuit breakers. They utilize a bimetallic strip for thermal protection and an electromagnet for magnetic protection. This combination ensures efficient and reliable protection against overloads and short circuits.
These circuit breakers are commonly used in critical applications where both thermal and magnetic protection is required. The bimetallic strip provides accurate and precise tripping for overloads, while the electromagnet offers fast and instantaneous response for short circuits. Hybrid circuit breakers are often found in sensitive equipment and systems that require reliable and comprehensive protection.
In conclusion, circuit breakers play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and integrity of electrical systems. Thermal circuit breakers, magnetic circuit breakers, and hybrid circuit breakers are just a few examples of the different types available. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications. Understanding the operating principles and features of these circuit breakers can help in selecting the right one for a particular electrical system.
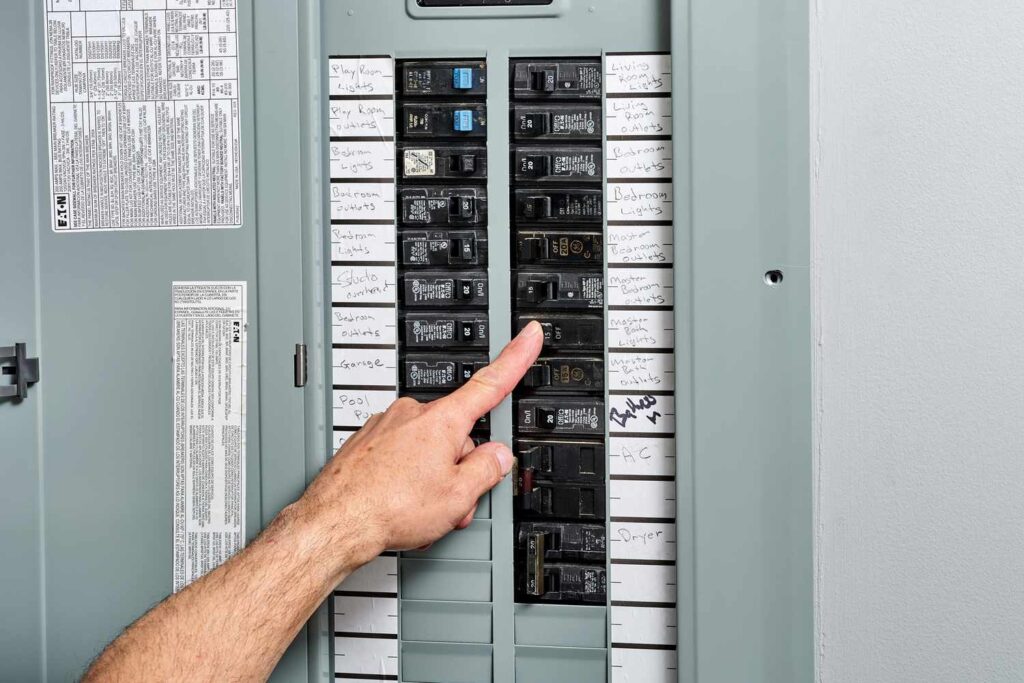

Understanding Circuit Breaker Functions
A circuit breaker is an essential component in any electrical system, providing protection against various electrical faults. It serves as a safety device, ensuring the smooth operation of electrical circuits and preventing potential damage to equipment and wiring. Let’s explore the different functions of a circuit breaker in more detail.
Overload Protection
One of the primary functions of a circuit breaker is overload protection. Electrical circuits are designed to carry a specific amount of current, and when that limit is exceeded, it can lead to overheating and potential damage. The circuit breaker acts as a guardian, constantly monitoring the current flow. When it detects excessive current, it opens the contacts, interrupting the circuit and preventing further damage. This crucial protection mechanism ensures the longevity and reliability of electrical systems.
Imagine a scenario where a circuit is powering multiple appliances simultaneously, drawing more current than it can handle. Without overload protection, the circuit would become overloaded, causing the wires to overheat and potentially leading to a fire. However, with a circuit breaker in place, it detects the excessive current and quickly shuts off the circuit, preventing any hazardous situations.
Short Circuit Protection
Short circuits are another common electrical fault that can occur due to a fault in the wiring or a malfunctioning electrical device. In a short circuit, a large amount of current flows through the circuit, bypassing the normal load. This sudden surge of current can cause severe damage to the electrical system and pose a significant safety risk.
Circuit breakers with short circuit protection are designed to detect and interrupt this excessive current flow. They are equipped with special mechanisms such as magnetic trip coils or electronic sensors that can quickly sense the abnormal current. Once detected, the circuit breaker trips, opening the contacts and cutting off the power supply to the faulty circuit. This rapid response prevents further damage and reduces the risk of electrical fires.
Consider a situation where a faulty wire comes into contact with a conductive surface, causing a short circuit. Without a circuit breaker with short circuit protection, the excessive current would continue to flow, potentially damaging the wiring and creating a hazardous situation. However, with the presence of a circuit breaker, it detects the abnormal current and swiftly interrupts the circuit, ensuring the safety of the electrical system and the people nearby.
Ground Fault Protection
Ground fault protection is another critical function of a circuit breaker. It is specifically designed to detect an unintended electrical path between a live wire and a ground source. This can occur when someone accidentally touches a live wire or when a wire comes into contact with a conductive surface, such as a metal casing or a wet area.
When a ground fault occurs, the circuit breaker with ground fault protection instantly trips, cutting off the power supply to the circuit. This rapid response is crucial in preventing electric shocks and protecting individuals from injuries. By interrupting the circuit, the circuit breaker eliminates the potential danger and ensures the safety of the electrical system.

Imagine a scenario where a faulty appliance develops a ground fault, causing the metal casing to become electrified. Without ground fault protection, anyone who touches the appliance could receive a severe electric shock. However, with a circuit breaker equipped with ground fault protection, it detects the unintended electrical path and immediately trips, preventing any harm to the individuals and maintaining the integrity of the electrical system.
In conclusion, circuit breakers play a vital role in safeguarding electrical systems from various faults. Whether it is overload protection, short circuit protection, or ground fault protection, these functions ensure the smooth operation of electrical circuits and protect against potential hazards. Understanding the functions of circuit breakers is essential for anyone working with electrical systems, as it promotes safety and prevents damage to equipment and wiring.
Selecting the Right Circuit Breaker
Considerations for Choosing a Circuit Breaker
When selecting a circuit breaker, several factors should be taken into account. The current rating, voltage rating, and trip characteristics should match the requirements of the electrical circuit. Additionally, considerations such as the type of load, environmental conditions, and available space should be considered to ensure the circuit breaker is suitable for the application.
Safety Standards and Certifications
It is crucial to choose circuit breakers that meet safety standards and certifications to ensure their reliability and performance. Look for circuit breakers that comply with recognized industry standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) standards or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Circuit Breakers
Common Circuit Breaker Issues
Like any electrical component, circuit breakers can experience problems over time. Some common issues include tripping for no apparent reason, failure to trip during faults, or difficulty resetting. It is important to address these issues promptly to ensure the continuous and reliable functioning of the electrical system.
Tips for Maintaining Your Circuit Breaker
Maintaining circuit breakers is essential to ensure their optimal performance. Regular inspections, cleaning, and testing are recommended. Inspect for any signs of damage, such as corrosion or loose connections, and promptly address them. Additionally, exercising the breaker periodically can help maintain its functionality and reliability.In conclusion, understanding the types and functions of circuit breakers is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. By selecting the right circuit breaker, adhering to safety standards, and carrying out regular maintenance, you can ensure the smooth operation of your electrical circuits and protect your equipment and premises from potential hazards.